SEC
26
Applications of TSKgel PW-type Gel Filtration columns
Polysaccharides
TSKgel PW columns are recommended for polysaccharide analysis
due to their ability to separate a wide molecular weight distribution.
Nonionic polysaccharides are the least complicated molecules to
analyze by SEC because they seldom exhibit secondary interactions
with the solid support. TSKgel G5000PW and TSKgel G3000PW in series
are effective for the characterization of clinical dextran.
Cationic samples can be adsorbed on the resin by electrostatic
interaction. If the polymer is strongly cationic, a fairly high salt
concentration is required to prevent ionic interactions with conventional
SEC packings. A mobile phase of 0.5 mol/L acetic acid with 0.3 mol/L
Na
2
SO
4
can also be used.
The new TSKgel PW
XL
-CP series enables elution of water soluble,
cationic polymers under low salt conditions (e.g. 0.1 mol/L NaNO
3
). An
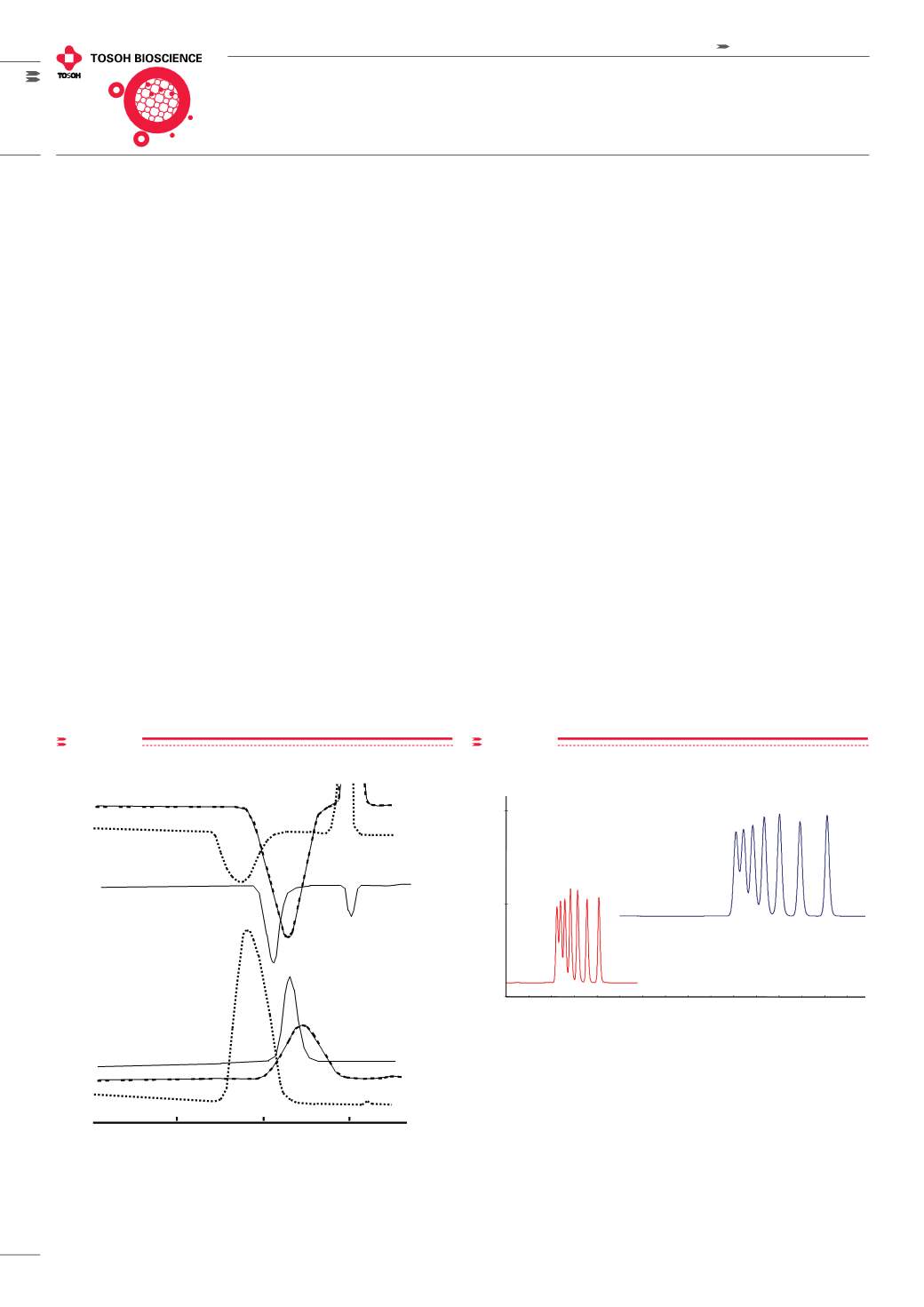
effective separation of the anionic hydrophilic gluco-saminoglycan,
hydraluronic acid, is shown in
Figure 22
on a TSKgel G6000PW and
TSKgel G4000PW column in series with a 0.2 mol/L sodium chloride
mobile phase.
Column: TSKgel G6000PW + G4000PW, two 7.5 mm ID x 60 cm L columns in
series; Mobile phase: 0.2 mol/L NaCl; Flow rate: 0.9 mL/min
Temperature: 40°C; Samples: hyaluronic acid
Oligosaccharides
FIGURE 23
shows the rapid analysis of maltose oligomers using a
TSKgel SuperOligoPW column compared to a TSKgel G-Oligo-PW
column. The faster analysis time is due to the semi-micro dimensions
(6.0 mm ID x 15 cm L) and the small particle size (3 μm) of the TSKgel
SuperOligoPW column compared to the 7.8 mm ID x 30 cm L size and 7
μm particle size of the TSKgel G-Oligo-PW column.
Column: A: TSKgel SuperOligoPW, 3 μm, 6.0 mm ID x 15 cm L x 4
B: TSKgel G-Oligo-PW, 7 μm, 7.8 mm ID x 30 cm L x 4; Mobile phase: H
2
O
Flow rate: A: 0.6 mL/min B: 1.0 mL/min; Detection: RI; Temperature: 40°C
Injection vol.: A: 10 μL B: 50 μL; Samples: 1.maltoheptose, 2. maltohexose,
3. maltopentose, 4. maltotetraose, 5. maltotriose, 6. maltose, 7. glucose
figure 23
Analysis of maltose oligomers
figure 22
Analysis of oligosaccharides
Columns:
A: TSKgel SuperOligoPW, 6.0m ID x 15cm x 4
B: TSKgel G-Oligo-PW, 7.8mm ID x 30cm x 4
Mobile phase: H
2
O
Flow rate:
A: 0.6mL/min B: 1.0mL/min
Detection:
RI
Temperature: 40
°
C
Injection vol.: A: 10µL B: 50µL
Samples: 1. maltoheptose 2. maltohexose 3. maltopentose
4. maltotetraose 5. maltotriose 6. maltose
7. glucose
0
50
100
10
14
18
22
26
30
34
38
42
mV
Elution time (minutes)
1
7 6
54
32
A
B
30
45
Minutes
Sample:
Mobile phase:
Flow Rate:
Temp:
TSKgel G6000PW + G4000PW, two 7.5mm ID x 60cm
columns in series
hyaluronic acid
0.2mol/L NaCl
0.9mL/min
40°C
15
0
1
2
3
1. Hyaluronic acid
2. Hyaluronic acid
3. Polyethylene oxide SE30
RI
LS


