Iec
IEC
51
Silica-based Anion Exchange Columns
TSKgel 2SW-type columns provide high performance separations
of small ionic solutes. The increased solubility of the silica backbone
above pH 7 limits the use of the TSKgel 2SW-type columns to acidic or
neutral mobile phases. This restricts method development and requires
special cleaning procedures when compared to the more robust TSKgel
5PW-type polymer-based columns.
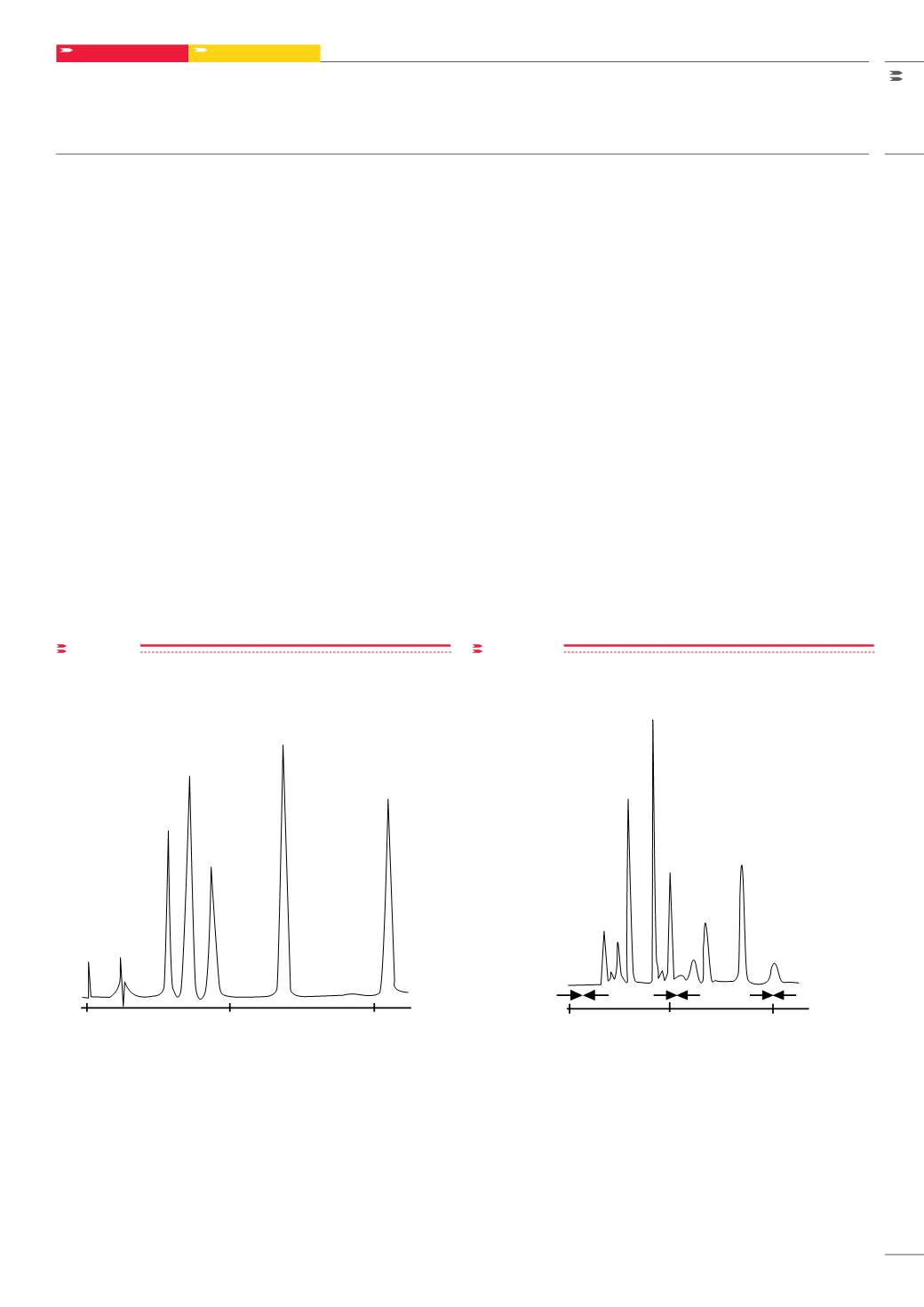
High performance analyses of small anionic species are best performed
on small pore silica-based anion exchangers, such as TSKgel DEAE-
2SW. This is demonstrated in
Figure 7
.
The 25 nm pore size TSKgel
DEAE-3SW column is used for separating peptides, low MW proteins
and DNA fragments.
Column: TSKgel DEAE-2SW, 4.6 mm ID x 25 cm L; Sample: 1. AMP, 2. IMP,
3. GMP, 4.ADP, 5. ATP; Buffer A: ACN in 0.1 mol/L phosphate, pH 3.0, 20/80;
Buffer B: ACN in 0.5 mol/L phosphate, pH 3.0, 20/80; Elution: 30 min linear
gradient from buffer A to B; Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min; Detection: UV @ 260 nm
Specialty Columns
Analyses of monosaccharides, disaccharides, and sugar alcohols can
be performed on PS-DVB columns, either by isocratic (TSKgel Sugar
AXI) or by gradient (TSKgel Sugar AXG) analysis. Saccharides are
retained on Sugar AX columns following the formation of negatively
charged complexes with boric acid at alkaline pH.
Figure 8
shows the
separation of twelve mono- and di-saccharides.
The strong anion exchange TSKgel SAX column can be used for the
separation of isomerized sugars, alcohols, and low molecular weight
organic acids.
Column: TSKgel Sugar AXG, 4.6 mm ID x 15 cm L; Sample: disaccharides, 25
mmol/L; monosaccharides, 50 mmol/L: 1. cellobiose, 2. maltose, 3. lactose,
4. rhamnose, 5. lyxose, 6. ribose, 7. mannose, 8. fructose, 9. arabinose, 10.
galactose, 11. xylose, 12. glucose; Elution: step gradient: 6 min buffer A,
0.6 mol/L boric acid, pH 7.7; then 27 min buffer B, 0.7 mol/L boric acid, pH
7.25; then 30 min buffer C, 0.7 mol/L boric acid, pH 8.7; Flow rate: 0.4 mL/min
(column and post column reagent solution); Pressure:16 kg/cm
2
; Temperature:
70°C (column), 100 °C (post column reactor);
Detection: fluorescence excitation @331 nm, emission @383 nm;
PC reagent: 2.5 % 2-cyanoacetamide solution
figure7
Separation of nucleotides on TSKgel DEAE-2SW
figure 8
Separation of saccharide mixture on TSKgel Sugar AXG
Separation of saccharide mixture on TSKgel Sugar AXG
0
30
60
Minutes
Column:
Sample:
Elution:
Flow Rate:
Pressure:
Temperature:
Detection:
PC reagent:
TSKgel Sugar AXG, 4.6mm ID x 15cm
disaccharides, 25mmol/L; monosaccharides,
50mmol/L: 1. cellobiose, 2. maltose, 3. lactose,
4. rhamnose, 5. lyxose, 6. ribose, 7. mannose,
8. fructose, 9. arabinose, 10. galactose,
11. xylose, 12. glucose
step gradient: 6min buffer A, 0.6mol/L boric acid,
pH 7.7; then 27min buffer B, 0.7mol/L boric acid,
pH 7.25; then 30min buffer C, 0.7mol/L boric acid, pH 8.7
0.4mL/min (column and post column reagent solution)
16kg/cm
2
70ºC (column), 100ºC (p st column reactor)
fluorescence excitation @ 331nm,
emission @ 383nm
2.5% 2-cyanoacetamide solution
Buffers:
A
B
C
A
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
Separation of nucleotides on TSKgel DEAE-2SW
0
24
Minutes
Column:
Sample:
Buffer A:
Buffer B:
Elution:
Flow Rate:
Detection:
TSKgel DEAE-2SW, 4.6mm ID x 25cm
1. AMP, 2. IMP, 3. GMP, 4.ADP, 5. ATP
ACN in 0.1mol/L phosphate, pH 3.0, 20/80
30 in linear gradi nt from buffer A to B
1.0mL/min
UV @ 260nm
1
2
3
4
5
12
ACN in 0.5mol/L phosphate, pH 3.0, 20/80
Applications of TSKgel ANION exchange columns


