TOSOH
CUSTOMER MAGAZINE
Michal Douša et al. [1] published an article in the Journal of Separa-
tion Science on quantification of structurally related aliphatic amino
alcohols in l-valinol. They used the popular TSKgel Amide-80 HILIC
phase for separation. HILIC separation was combined with postco-
lumn derivatization and fluorescence detection. L-Valinol is used as
intermediate product for production of elvitegravir, an integrase inhi-
bitor used to treat HIV infection. The amino alcohols in l-valinol were
effectively separated and quantified with the described method. The
influence of the mobile phase (salt type, buffer concentration, and pH)
on retention was studied. The TSKgel Amide column (150 × 4.6 mm,
3 µm) used in this study provided well-separated symmetric peaks of
analytes with a mobile phase consisting of 10 mM acetate buffer pH
4.0 and acetonitrile (20:80, v/v). After postcolumn derivatization with
o-phtaldialdehyde/2-mercaptoethanol fluorescence detection was
performed using at an excitation wavelength of 345 and an emission
wavelength of 450 nm. After validation, the method was successfully
applied to the analysis of commercial samples of l-valinol.
The group of Szabolcs Fekete evaluated hydrophobic interaction
chromatography for the separation of monoclonal antibodies and
antibody-drug-conjugate species and published two articles on their
findings in the Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis:
Part 1 focusing on the optimization of the mobile phase and part 2 on
the optimization of the phase system.
Part one published by Marta Rodriguez-Aller et al. [2] provides recom-
mendations for method development in HIC using monoclonal anti-
bodies (mAbs) and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) as model drug
candidates. The goal of part 2 published by Alessandra Cusumano et
al. [3] was to evaluate the performance of commercially available HIC
columns and to develop a fast and automated optimization procedure
for the analytical characterization of protein biopharmaceuticals. For
this purpose, various therapeutic mAbs (denosumab, palivizumab,
pertuzumab, rituximab and bevacizumab) and a cysteine linked ADC
(brentuximab-vedotin) were selected as model substances. Several
HIC column chemistries (butyl, ether and alkylamide) from different
vendors were evaluated in four different buffer systems (sodium ace-
tate, sodium chloride, ammonium acetate and ammonium sulfate).
TSKgel Butyl NPR was among the evaluated columns and found to
be one of the most versatile ones in terms of hydrophobicity, peak
capacity and achievable selectivity. As salt types, ammonium sulfate
and sodium acetate were found to be particularly well suited for the
analytical characterization of mAbs and ADCs.
TO LIKE OR DISLIKE WATER THAT IS THE QUESTION
AMONG THE MANY SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES PUBLISHED ABOUT RESEARCH PROJECTS INVOLVING TSKgel HPLC OR UHPLC COLUMNS WE
PICKED TWO VERY RECENT EXAMPLES. CHROMATOGRAPHIC MODES APPLIED WERE HYDROPHOBIC INTERACTION (HIC) AND HYDROPHI-
LIC INTERACTION LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY (HILIC).
07
TSKgel
IN THE LITERATURE
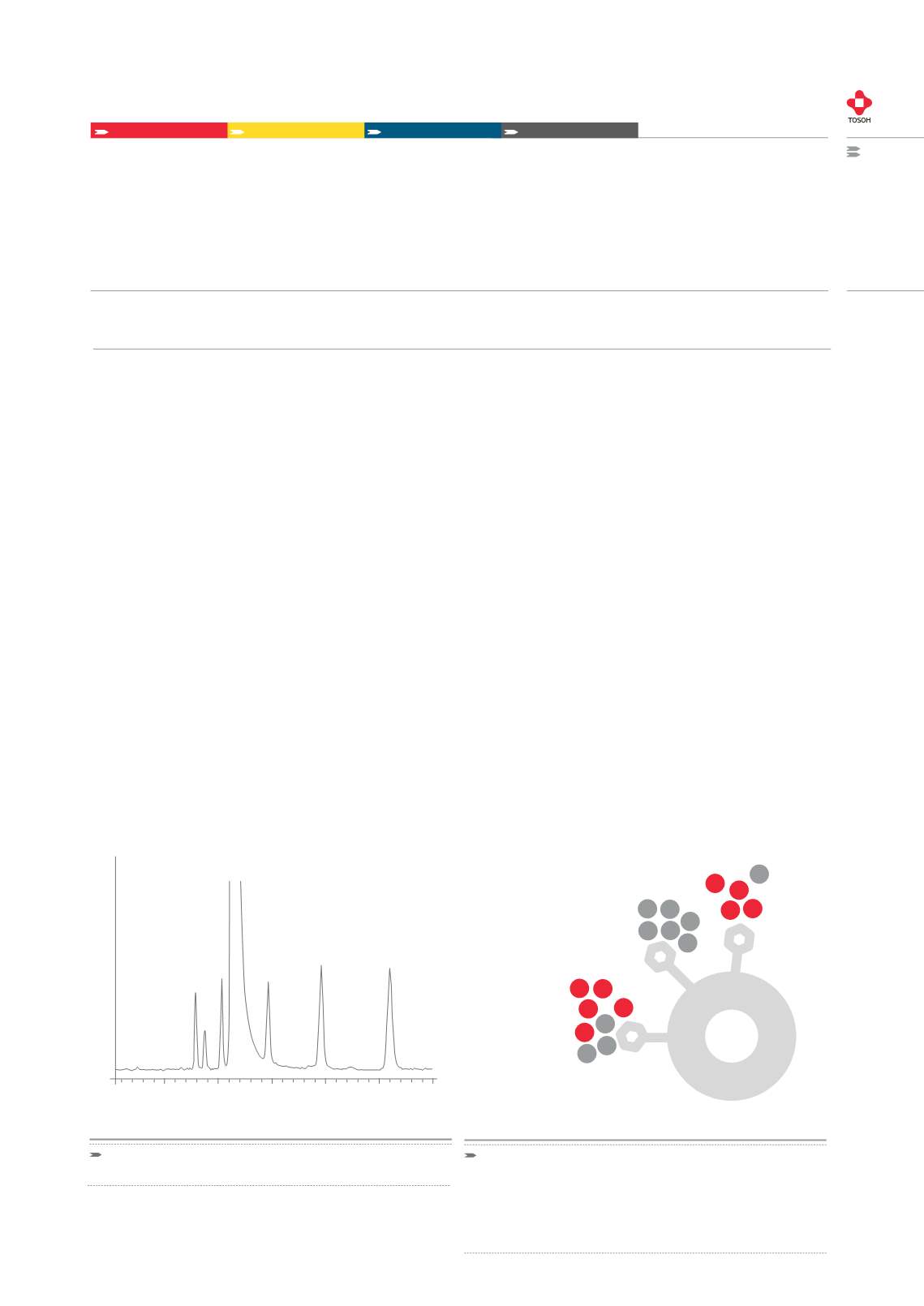
FIGURE 1:
SEPARATION OF AMINO ALCOHOLS ON TSKgel AMIDE HILIC
COLUMN AS SHOWN IN REFERENCE 1
5.0
10.0
15.0
20.0
25.0
30.0
Retention time
[min]
Detector response
Leuclnol
Isoleuclnol
Valinol
2-Amino-1-pentanol
2-Amino-1-butanol
2-Amino-1-propanol
Ethanolamine
⇒REFERENCES:
[1]
DOUŠA, M., STACH, J., GIBALA, P., AND LEMR, K. (2016) J. SEP. SCIENCE
MAR;39(5):851-6; DOI: 10.1002/JSSC.201501302
[2]
RODRIGUEZ-ALLER, M., GUILLARME, D., BECK, A., AND FEKETE, S. (2016) J
PHARM BIOMED ANAL. 118:393-403; DOI: 10.1016/J.JPBA.2016.11.011
[3]
CUSUMANO, A., GUILLARME, D., BECK, A., AND FEKETE S. (2016) J PHARM BIO-
MED ANAL. 121:161-73; DOI: 10.1016/J.JPBA.2016.01.037


